Dalia Savy
Dalia Savy
AP Psychology 🧠
334 resourcesSee Units
Answers and Review for Multiple Choice Practice on Social Psychology
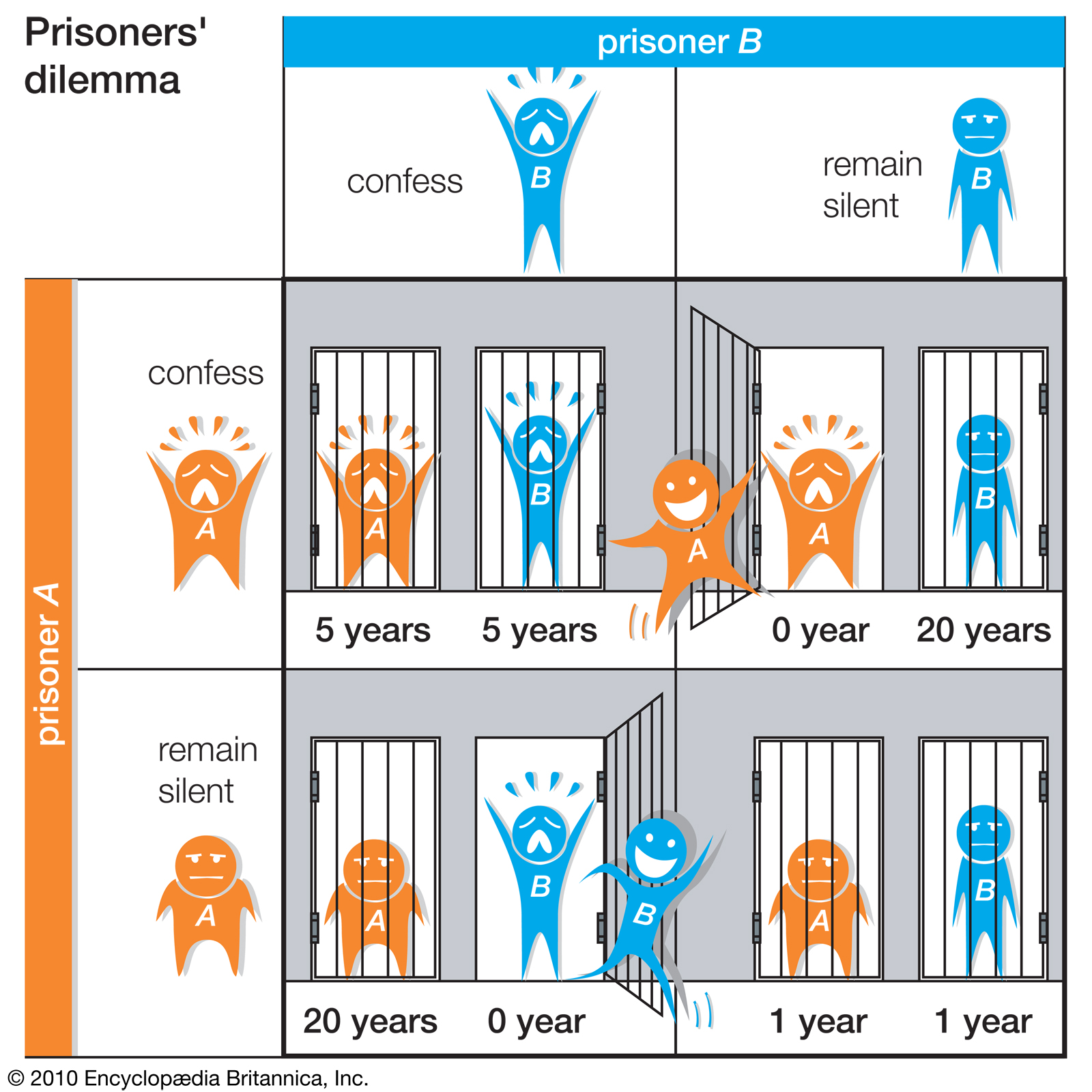
Image Courtesy of Britannica.
Here is an example of a social trap, called the Prisoner’s dilemma. Social traps cause us to harm the well-being of society for our own interests.
⛔STOP!⛔ Before you look at the answers make sure you gave this practice quiz a try so you can assess your understanding of the concepts covered in unit 9. Click here for the practice questions: AP Psychology Unit 9 Multiple Choice Questions.
Facts about the test: The AP Psychology exam has 100 multiple choice questions and you will be given 1 hour and 10 minutes to complete the section. That means it should take you around 11 minutes to complete 15 questions.
*The following questions were not written by CollegeBoard and although they cover information outlined in the AP Psychology Course and Exam Description, the formatting on the exam may be different.
1. The more one is exposed to something, the more one will come to like it. "Familiarity breeds acceptance." This description relates to which of the following terms:
A. Central Route of Persuasion
B. Compliance
C. Self-Serving Bias
D. Mere-Exposure Effect
Answer: Self-serving bias is the tendency to take credit for good outcomes than bad ones. The central route of persuasion involves being persuaded based on the content of the message, and compliance is acquiescing to another's request.
📄 Study AP Psychology, Unit 9.5: Bias, Prejudice, and Discrimination
2. A compliance strategy when a small request is followed by a larger request is called:
A. Door-in-the-Face
B. Foot-in-the-Door
C. Deindividuation
D. Low-balling
Answer: Deindividuation is not a compliance technique. It is illustrated in large groups when persons lose self-constraint when they feel anonymous and aroused. Door-in-the-Face is when a large request is denied and followed by a smaller request which actually is the target of the request. Low balling is a compliance method when the persuader gets a person to agree to a low ball offer they have no intention of keeping and then increases the price. Often used in sales.
📄 Study AP Psychology, Unit 9.2: Attitude Formation and Attitude Change
3. The biased belief that people get what they deserve and deserve what they get is called:
A. Prejudice
B. False-Consensus Effect
C. just-world bias or phenomenon
D. In-group bias
Answer: False consensus is a tendency for people to overestimate the number of people who agree with them. Prejudice is an attitude, usually negative, towards a particular group of people, and in-group bias stems from a belief that the group to whom a person belongs is thought to be good. Just world we assume we are good and that bad things happen to people because they somehow brought it on themselves. EX: people are unemployed because they are lazy. We are not lazy; therefore, we are not unemployed.
📄 Study AP Psychology, Unit 9.1: Attribution Theory and Person Perception
4. Which is the best example of social facilitation?
A. A pianist plays a well-learned and practiced Beethoven piece in front of a large audience flawlessly.
B. A pianist performs a difficult piece in front of a large audience and makes many mistakes.
C. You jump into a conversation that has already started and are told, "We are talking about something else." After an awkward silence, you look around the room nervously certain everyone else has heard.
D. Working in a group and one of the members does not put in much effort and is less motivated to provide input or do his/her share.
Answer: Playing a difficult piece and messing up in front of a large audience is social impairment. Jumping in and getting "told" and feeling as if everyone is looking at you is the spotlight effect. Working in a group example describes social loafing.
📄 Study AP Psychology, Unit 9.4: Group Influences on Behavior and Mental Processes
5. The primary reason bystanders in the Kitty Genovese crime did nothing is...
A. Groupthink
B. Diffusion of responsibility
C. Fundamental Attribution Error
D. Cognitive Dissonance Theory
Answer: Groupthink occurs when members of the group desire harmony over critical thinking in decision making. Fundamental attribution error is to overestimate another's dispositional factor and underestimate situational factors. Cognitive dissonance occurs when a person has inconsistent attitudes and behaviors which causes them discomfort and mental tension. In the case of Kitty Genovese, as she was being attacked, many heard her screams but believed others would intervene or call the police. A diffusion of responsibility is the tendency for people to assume someone else will take action so they do not need to do so.
📄 Study AP Psychology, Unit 9.6: Altruism and Aggression
6. Which of the following is not an accurate description of collectivist cultures?
A. Interdependent
B. Us-group goals and solidarity
C. Independent
D. Behavior reflects social norms and roles
Answer: Individualistic cultures are focused on independence and identity of individual traits, personal achievement, and behavior that reflects one's personality and attitudes. All the other options focus on a collectivist society.
📄 Study AP Psychology, Unit 7.8: Humanistic Theories of Personality
7. Belief that one's culture-ethnic group, racial group, etc… is superior to others is called:
A. ethnocentrism
B. in-group bias
C. prejudice
D. self-fulfilling prophecy
Answer: Although all of these answers are somewhat related, ethnocentrism specifically involves people from one culture becoming so entrenched in their own culture, that they see it as the standard by which members judge other cultures.
📄 Study AP Psychology, Unit 9.5: Bias, Prejudice, and Discrimination
8. Researcher who designed an experiment on obedience:
A. Solomon Asch
B. Phil Zimbardo
C. Leon Festinger
D. Stanley Milgram
Answer: In 1963, Stanley Milgram's famous shock machine experiment tested the effects of conflict between obedience to authority and personal conscience. He set up "teachers" the actual subjects and "learners" who were confederates in the experiment. Teachers gave the learners a "shock" from a fake shock machine, for every wrong answer. 65% of the teachers went up to the highest shock level- 450 volts when told by the authority figure, "Please continue." This experiment is unethical due to its deception and undue stress and harm to the teachers.
📄 Study AP Psychology, Unit 9.3: Conformity, Compliance, and Obedience
9. Researcher who carried out an experiment on conformity:
A. Solomon Asch
B. Stanley Milgram
C. Philip Zimbardo
D. Walter Mischel
Answer: Asch's subjects believed they were taking a line acuity test when they were actually taking part in an experiment to measure conformity to group pressure.
📄 Study AP Psychology, Unit 9.3: Conformity, Compliance, and Obedience
10. Researcher who carried out an experiment on the power of dispositional vs situational factors and the effects of role-playing on attitudes is:
A. Leon Festinger
B. Muzafer Sherif
C. Philip Zimbardo
D. Walter Mischel
Answer: Zimbardo's famous Stanford Prison experiment took place in the psychology building of the university in 1973. Subjects were randomly assigned to the role of prisoner or prison guard in a simulated prison environment. The experiment which was to last 2 weeks ended after 6 days due in part to Zimbard's lack of objectivity and the undue stress and harm carried out by the guards on the prisoners.
📄 Study AP Psychology, Unit 9.3: Conformity, Compliance, and Obedience
11. Fred did very poorly on an algebra test. The tendency to make the fundamental attribution error might lead his sixth-grade teacher to conclude that Fred did poorly because...
A. the test covered material that had not been adequately covered in class.
B. he was not given enough time to complete the test.
C. his parents had an argument the evening before the test.
D. he is unmotivated to do well in school.
Answer: Fred's teacher explains his poor performance on the math test as a dispositional factor-unmotivated-vs any situational factors described in the other answer choices.
📄 Study AP Psychology, Unit 9.1: Attribution Theory and Person Perception
12. Following the 9/11 terrorist attack on New York, people across the country donated their time and money to assist the devastated community. This behavior best illustrates...
A. bystander intervention effect
B. social exchange theory
C. altruism
D. just world phenomenon
Answer: Altruism is behavior motivated by helping others selflessly without seeking benefit for one's own self.
📄 Study AP Psychology, Unit 9.6: Altruism and Aggression
13. When someone invites you to their home for dinner, you feel obligated to do the same at a later date. This description illustrates:
A. just world phenomenon
B. reciprocity norm
C. foot-in-the-door
D. social exchange theory
Answer: Reciprocity norm suggests that humans need to reciprocate in kind the action of another person.
📄 Study AP Psychology, Unit 9.6: Altruism and Aggression
14. A gradual escalation of intimacy is most positively related to a gradual escalation of
A. reciprocity norm
B. cognitive dissonance
C. self-disclosure
D. normative social influence
Answer: Self-disclosure is a process of communication when a person reveals and shares with another personal information such as dreams, thoughts, feelings, fears, goals, etc...It often leads to intimacy if it is reciprocated.
📄 Study AP Psychology, Unit 9.7: Interpersonal Attraction
15. Conformity resulting from a person's desire to gain approval or avoid disapproval is said to be a response to
A. normative social influence
B. informational social influence
C. groupthink
D. social facilitation
Answer: Normative and informational social influence are two reasons why people conform to a group. Normative is to change one's mind or behavior to"fit in" with the group. Informational is when a person may lack knowledge or expertise and looks to the group for guidance and goes along for that reason.
📄 Study AP Psychology, Unit 9.3: Conformity, Compliance, and Obedience
Connect with other students studying AP Psychology with Hours
Browse Study Guides By Unit
🔎Unit 1 – Scientific Foundations of Psychology
🧠Unit 2 – Biological Basis of Behavior
👀Unit 3 – Sensation & Perception
📚Unit 4 – Learning
🤔Unit 5 – Cognitive Psychology
👶🏽Unit 6 – Developmental Psychology
🤪Unit 7 – Motivation, Emotion, & Personality
🛋Unit 8 – Clinical Psychology
👫Unit 9 – Social Psychology
✏️Frequently Asked Questions
🧐Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ)
✍️Free Response Questions (FRQ)
📆Big Reviews: Finals & Exam Prep

© 2023 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.