AP Physics 1 🎡
257 resourcesSee Units
AP Physics 1 Free Response Question on Energy
👋 Welcome to the AP Physics 1 Unit 4 FRQ (Energy). These are longer questions, so grab some paper and a pencil, or open up a blank page on your computer. After you finish, you can see how you did with Unit 4 FRQ (Energy) Answers.
⏱ The AP Physics 1 exam has 5 free-response questions, and you will be given 90 minutes to complete the FRQ section. (This means you should give yourself ~18 minutes to go through each practice FRQ.)
- 🤔 Need a quick refresher of the unit as a whole? Check out the Unit 4 Overview.
- 😩 Getting stumped halfway through answering? Look through all of the available Unit 4 Resources.
Setup
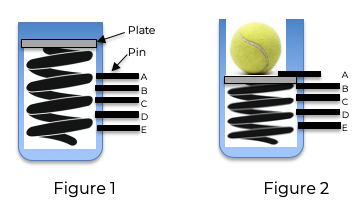
A projectile launcher consists of a spring with an attached plate, as shown in Figure 1. When the spring is compressed, the plate can be held in place by a pin at any of five positions A, B, C, D, or E.
For example, Figure 2 shows a ball placed against the plate, which is held in place by a pin at position A. The ball is launched upon release of the pin.
A student hypothesizes that the spring constant can be determined by launching the ball using different compression distances.
Questions
Part A
The student plans to test the hypothesis by launching the sphere using the launcher.
(i) State a basic physics principle or law the student could use in designing an experiment to test the hypothesis.
(ii) Using the principle or law stated in part (a) (i), determine (derive) an expression (physics equation) for the spring constant in terms of quantities that can be obtained from measurements made with equipment usually found in a school physics laboratory.
Part B
Design an experimental procedure to test the hypothesis in which the student uses the launcher to launch the ball. Assume equipment usually found in a school physics laboratory is available.
(i) In the table below, list the quantities and associated symbols that would be measured in your experiment. Also, list the equipment that would be used to measure each quantity. (You do not need to fill in every row. If you need additional rows, you may add them to the space just below the table.)
| Quantity to be Measured | Symbol for Quantity | Equipment for Measurement |
(ii) Describe the overall procedure to be used to test the hypothesis that the spring constant can be determined by launching the ball using different compression distances, referring to the table. Provide enough detail so that another student could replicate the experiment, including any steps necessary to reduce experimental uncertainty. As needed, use the symbols defined in the table and/or include a simple diagram of the setup.
Part C
The student completes the experiment and obtains the data below. Using the data that most closely matches your experimental procedure, determine the spring constant for the spring.
Mass of Tennis Ball: 0.056 kg
| Pin Location | Compression (m) | Maximum Height of Ball After Launch (m) | Maximum Launch Speed of Ball Exiting Launcher (m/s) |
| A | 0.1 | 0.31 | 2.45 |
| B | 0.2 | 1.22 | 4.90 |
| C | 0.3 | 2.76 | 7.35 |
| D | 0.4 | 4.90 | 9.80 |
| E | 0.5 | 7.65 | 12.2 |
(i) Using your expression in part (a) (ii), calculate the values that need to be plotted to find the spring constant for the spring and enter them into the data table above.
(ii) Using the graph below, plot data from the data table that will allow the student to find the value for the spring constant.

(iii) Using your best-fit line, determine the spring constant for the spring in the space provided below.
Answers & Rubric
💯 Ready to see how you did? Take a look at the Unit 4 FRQ (Energy) Answers.
Browse Study Guides By Unit
👟Unit 1 – Kinematics
🌀Unit 2 – Dynamics
🚀Unit 3 – Circular Motion & Gravitation
⚡️Unit 4 – Energy
⛳️Unit 5 – Momentum
🎸Unit 6 – Simple Harmonic Motion
🎡Unit 7 – Torque & Rotational Motion
💡Unit 8 – Electric Charges & Electric Force
🔋Unit 9 – DC Circuits
🔊Unit 10 – Mechanical Waves & Sound
📚Study Tools
🧐Exam Skills

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.