Dylan Black
Dalia Savy
Dylan Black
Dalia Savy
AP Chemistry 🧪
269 resourcesSee Units
Reactions in Aqueous Solution
When dealing with chemical reactions, it is important to understand that, at least in the case of AP Chemistry, the vast majority of them will be taking place in an aqueous solution, that is, dissolved in water💧. Therefore, we will not be dealing with molecules, but rather their constituent particles that are created when they dissolve.
Let's take NaCl🧂 for example. When you dissolve table salt in water, it is essentially ripped apart by the water molecules. It is important to understand that water is a polar molecule. Polar molecules have a partial positive end and a partial negative end. Therefore, when an ionic compound like NaCl dissolves, the water molecules rip it apart and trap it, per se.
In other words, ionic compounds dissociate into their ions when dissolved in water. To tie this back to unit three and intermolecular forces, when you dissolve NaCl, you will see ion-dipole interactions. The positive end of the water molecule (hydrogen) is attracted to the negative chloride anion, while the negative end of the water molecule (oxygen) is attracted to the positive sodium cation.
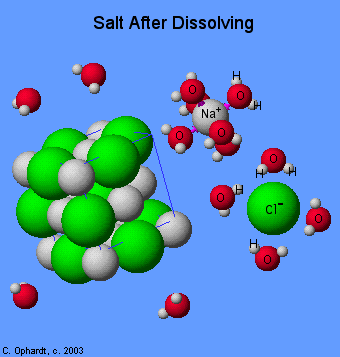
We can write out the dissolution of salt as NaCl (s) → Na⁺ (aq) + Cl⁻ (aq). Thus, if we have a reaction between two compounds in water, it will be the ions/parts of the molecules that dissolve that react together rather than the entire compounds themselves.
Let's look at a specific class of such reaction:
Precipitation Reactions
Sometimes, when two reactants react, one of the products is insoluble. To be insoluble means that it will NOT be ripped apart by water like NaCl would be. In other words, an insoluble product is one that precipitates out as a solid and does not dissolve in water.
One example of a precipitation reaction where one product is insoluble is the precipitation of lead (II) iodide:
2KI (aq) +Pb(NO₃)₂ (aq) → 2KNO₃ (aq) + PbI₂ (s).
Because lead (II) iodide is not soluble in water (according to the general solubility rules linked above), it precipitates and falls out of the solution.
Here is another table of solubility rules, but you do not need to memorize every single one of these. College Board has stated that only the following solubility rule will be assessed on the AP exam: "All sodium, potassium, ammonium, and nitrate salts are soluble in water."
Image Courtesy of Regents Chemistry Reference Table
Writing Net Ionic Equations
A net ionic equation is a chemical equation that shows only the species participating in a chemical reaction and omits the spectator ions. Spectator ions are ions that appear on both sides of the arrow in a chemical equation but do not actually participate in the reaction. In precipitation reactions, spectator ions are those that did not participate in the formation of the precipitate, or solid product.
Example #1
Let's see these concepts in action with our previous reaction: 2KI (aq) + Pb(NO₃)₂ (aq) → 2KNO₃ (aq) + PbI₂ (s)
If we write this reaction out with all of the ions, we get 2K⁺ (aq) + 2I⁻ (aq) + Pb²⁺ (aq) + 2NO₃⁻ (aq) → 2K⁺ (aq) + 2NO₃⁻ (aq) + PbI₂ (s). This was obtained by dissociating, or separating, each soluble compound into its constituent parts.
Note that PbI₂ does NOT dissociate, since it is insoluble. Be on the lookout for this! Only dissociate soluble compounds. Also, don't dissociate weak acids and bases🍊 (you'll learn more about this more in the future).
This equation, with the ions written out, is called the complete ionic equation or the total ionic equation. It shows every ion in the solution that is present during the reaction, including spectator ions.
Now let's take the spectator ions out of the reaction. When looking at the total ionic equation, we see that potassium and nitrate go in and come out the same way, so we can cross them out and cancel them. Potassium and nitrate were the spectator ions👓!
Once we eliminate the spectator ions, we are left with 2I⁻ (aq) + Pb²⁺ (aq) → PbI₂(s). This is what we call the net ionic equation for the reaction, and it tells us what really happens. Potassium and nitrate were in the flask, but they really didn't do much for us in terms of the formation of the insoluble compound. They could have been any suitable ion and the reaction would have had the same outcome.
General Steps
Now that you have an idea of what a net ionic equation is, it is time to learn how to write one out! First, you must know the basics of representing a chemical reaction. Make sure you review those in the last study guide before moving on.
To work through and learn this process, here are the general steps to writing a net ionic equation:
- Figure out which compounds are soluble and insoluble using solubility rules
- Balance the given chemical equation. It may already be balanced, but it also may not, so you always have to check.
- Write the complete ionic equation by dissociating soluble compounds into ions.
- Omit the spectator ions and write the final net ionic equation of the given reaction. Make sure you include the phase of matter each compound is in.
Example #2
Try writing the net ionic equation for the following reaction: KOH + Fe(NO₃)₃ → KNO₃ + Fe(OH)₃
- Using solubility rules, you should find that: Fe(OH)3 is the solid or the precipitate formed. Add the respective states of matter to each compound in the chemical equation.
- KOH (aq) + Fe(NO₃)₃ (aq) → KNO₃ (aq) + Fe(OH)₃ (s)
- You should notice that there is only 1 OH on left and 3 OH on the right. The same goes for NO3, but vice versa. This means we have to balance the equation.
- 3KOH (aq) + Fe(NO₃)₃ (aq) → 3KNO₃ (aq) + Fe(OH)₃ (s)
- Write out the complete ionic equation by dissociating all soluble compounds into their constituent ions. If you're ever unsure of what you should and shouldn't dissociate, remember that every compound in the aqueous solution will dissociate and the solid will not.
- 3K⁺ (aq) + 3OH⁻ (aq) + Fe⁺³ (aq) + 3NO₃⁻ (aq) → 3K⁺ (aq) + 3NO₃⁻ (aq) + Fe(OH)₃ (s)
- Identify the spectator ions by taking a look at what ions look the same before and after the chemical reaction took place or identifying which ions are not in the formed precipitate: 3K⁺ (aq) + 3OH⁻ (aq) + Fe⁺³ (aq) + 3NO₃⁻ (aq) → 3K⁺ (aq) + 3NO₃⁻ (aq) + Fe(OH)₃ (s)
- Write out your final answer and net ionic equation: 3OH⁻ (aq) + Fe⁺³ (aq) → Fe(OH)₃ (s)
Each of the above steps are different representations of a chemical reaction. Here is a quick summary of each of the terms that you should familiarize yourself with since the AP exam will expect you to know them:
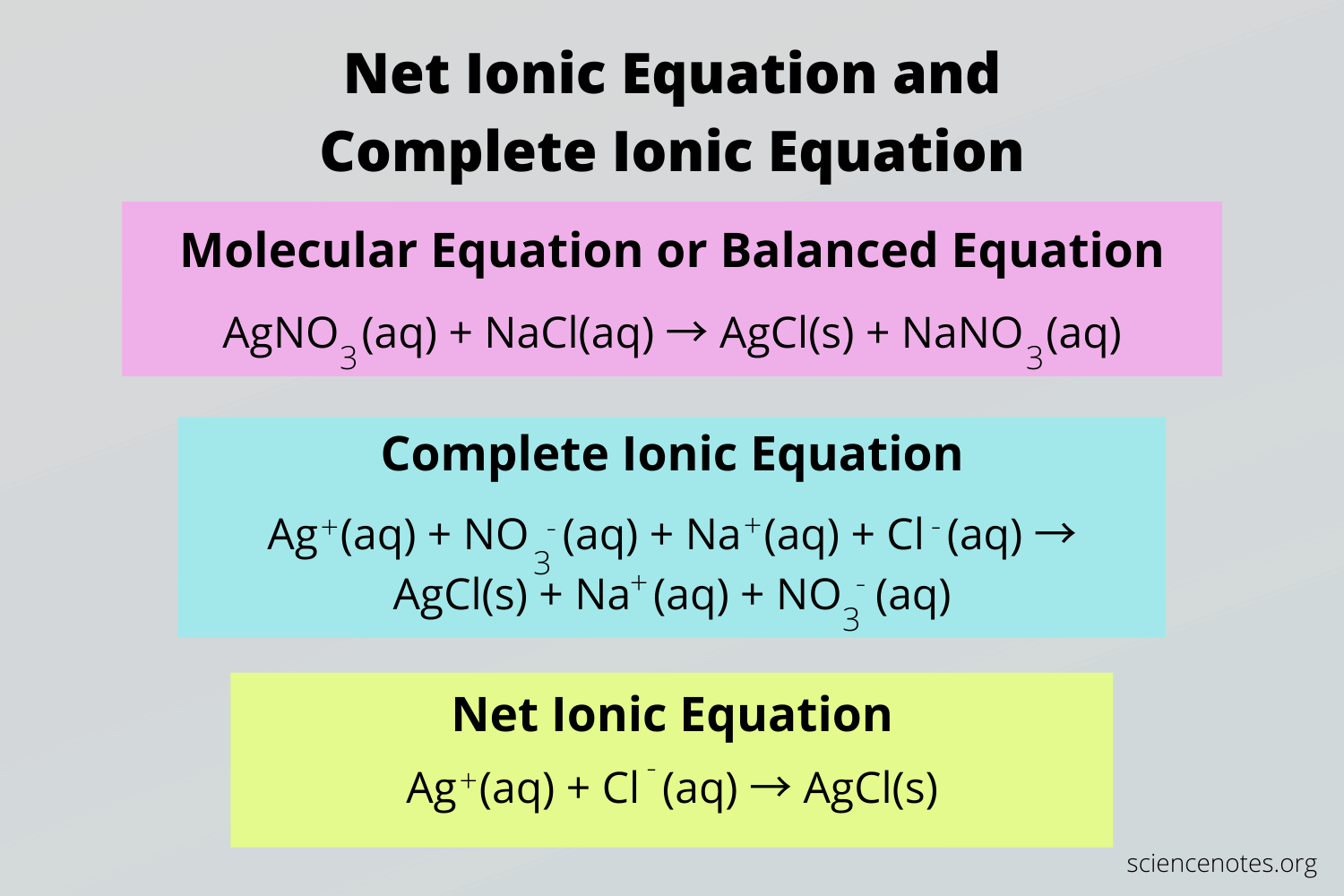
Image Courtesy of Science Notes
Browse Study Guides By Unit
⚛️Unit 1 – Atomic Structure & Properties
🤓Unit 2 – Molecular & Ionic Bonding
🌀Unit 3 – Intermolecular Forces & Properties
🧪Unit 4 – Chemical Reactions
👟Unit 5 – Kinetics
🔥Unit 6 – Thermodynamics
⚖️Unit 7 – Equilibrium
🍊Unit 8 – Acids & Bases
🔋Unit 9 – Applications of Thermodynamics
🧐Exam Skills
📚Study Tools

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.