9.2 Interactions Within and Across Cultures in Pacific Art
6 min read•june 18, 2024
Sylvia Rodriguez
Sylvia Rodriguez
AP Art History 🖼
34 resourcesStaff god
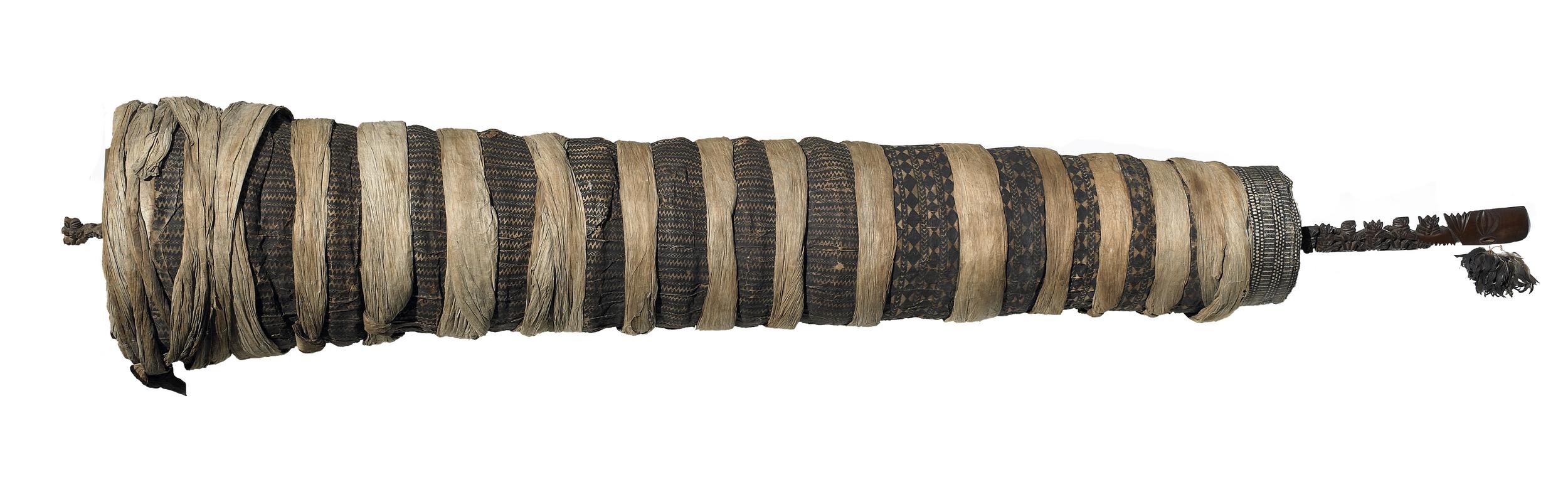

Staff-god in its barkcloth wrapping, late 18th–early 19th century, wood, paper mulberry bark, feather, 396 cm, Rarotonga, Cook Islands ( Trustees of the British Museum)
- A type of religious artifact used in Pacific Island cultures, such as those of Polynesia and Melanesia
- Represented a deity or spirit and served as a symbol of spiritual power
- Typically carved from wood and adorned with decorative elements such as feathers, shells, and other natural materials
- Used in religious rituals and ceremonies to communicate with the gods, request their protection, or seek blessings
- Can reflect the cultural beliefs, spiritual practices, and artistic traditions of Pacific Island societies.
- The design, style, and materials used in a staff god can provide insight into the cultural context in which it was created and used.
- Staff gods often represented male deities and were considered symbols of masculinity and power, reflecting the patriarchal nature of many Pacific Island societies.
- Staff gods can provide important information about the spiritual and cultural beliefs of Pacific Island peoples and their relationships with the gods and spirits they worshiped.
Buk (mask)
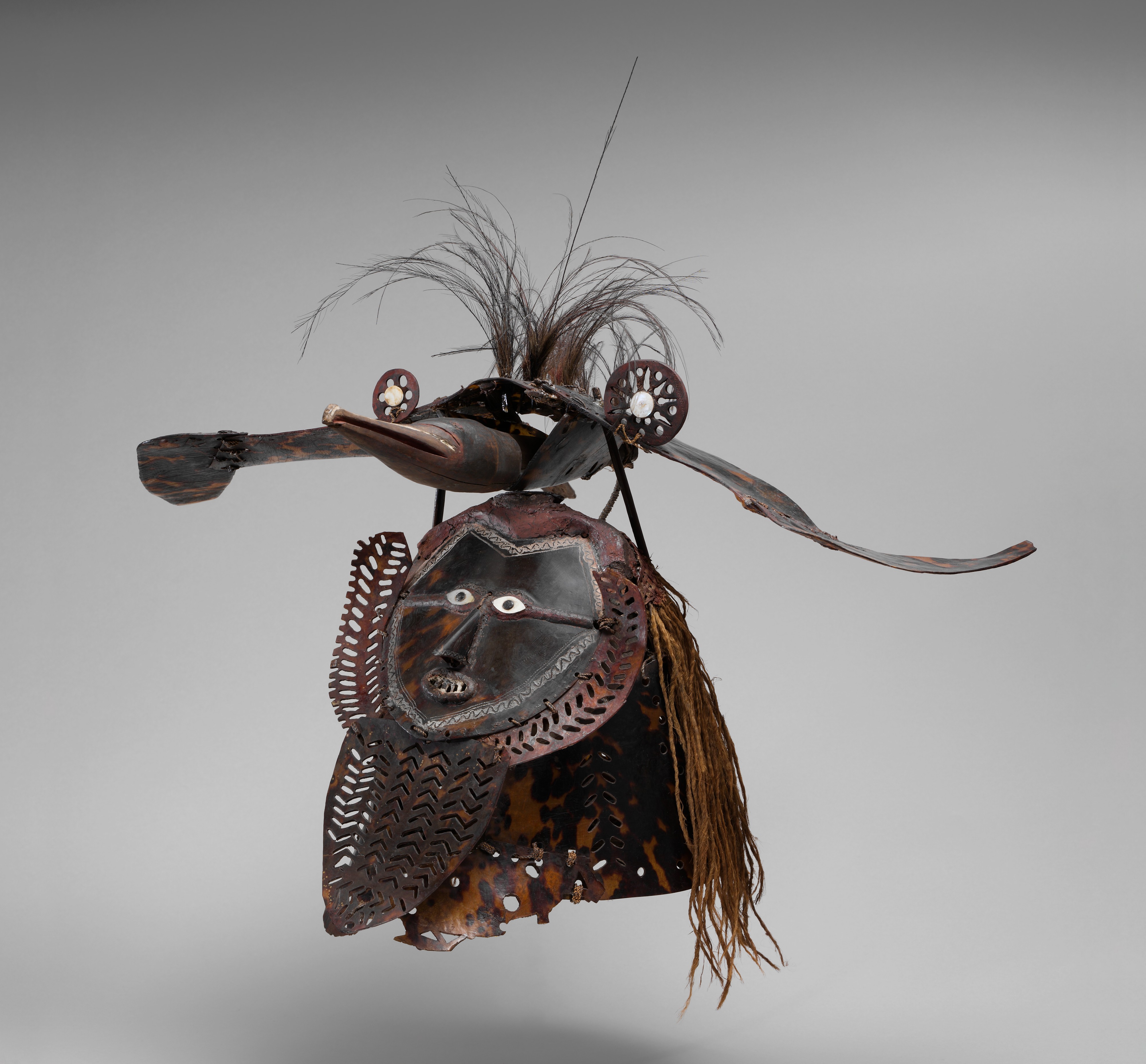

Mask (Buk), Torres Strait, Mabuiag Island, mid to late 19th century,turtle shell, wood, cassowary feathers, fiber, resin, shell, paint, 21 1/2 inches high (The Metropolitan Museum of Art)
- A specific type of Buk mask originating from the Torres Strait Islands, located between the northern coast of Australia and southern coast of Papua New Guinea
- The Torres Strait Islands have a rich cultural heritage, and the Buk masks made there reflect the unique blend of indigenous and colonial influences found in the region
- Buk masks from the Torres Strait are typically carved from wood and feature intricate designs, including patterns and imagery inspired by the local flora and fauna, as well as cultural motifs from the surrounding region.
- These masks were often used in traditional dances, ceremonies, and other cultural events, and could serve a variety of purposes, including storytelling, spiritual communication, and cultural preservation.
- The use of specific materials, such as the intricate shell and pearl inlays that are often found on Buk masks from the Torres Strait, is an important part of their cultural significance.
- Buk masks from the Torres Strait represent a unique form of Pacific Island art and can provide important insights into the cultural, spiritual, and historical context of the Torres Strait Islands and the surrounding region.
Tamati Waka Nene
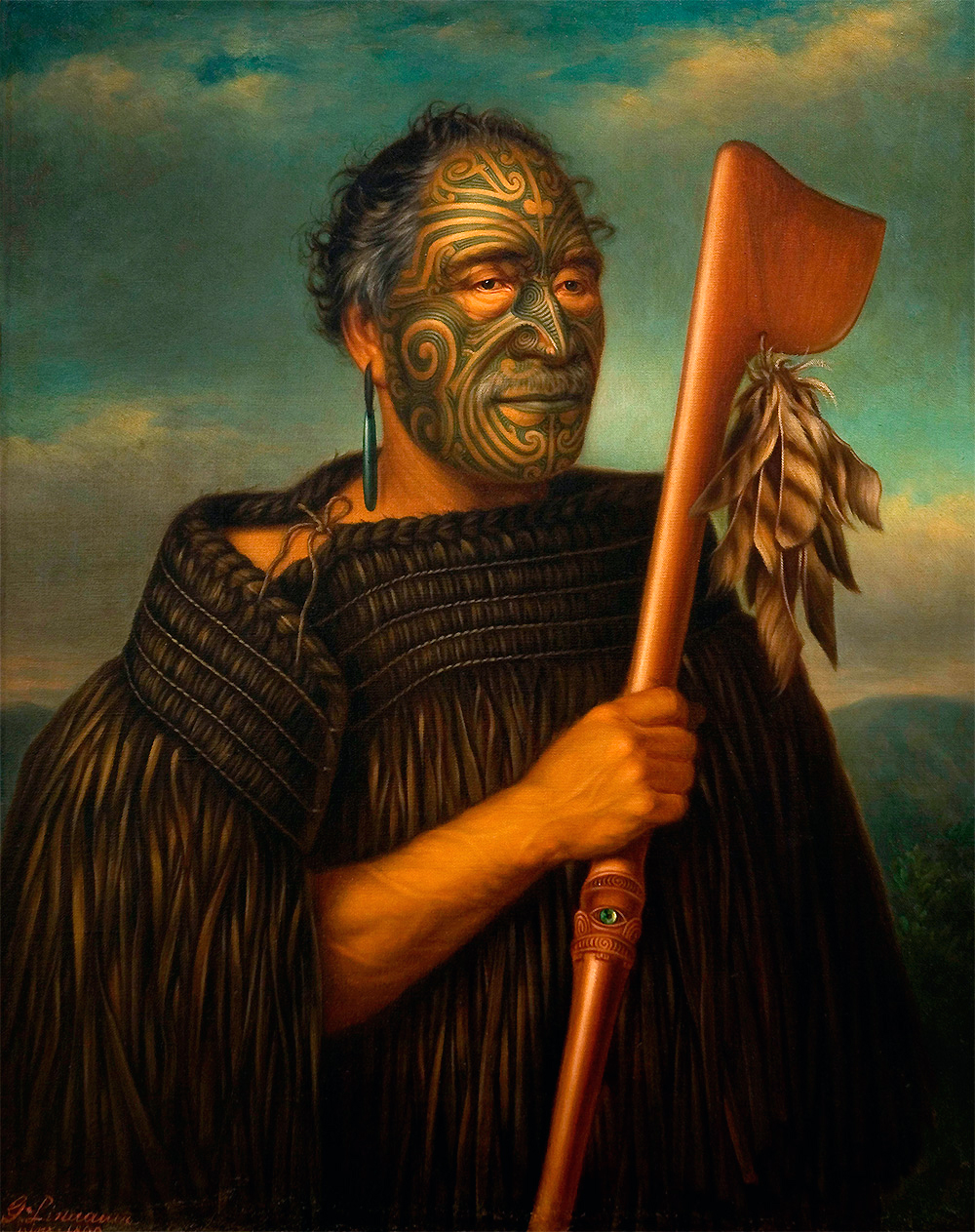

Gottfried Lindauer, Tamati Waka Nene, 1890, oil on canvas, 101.9 x 84.2 cm (Auckland Art Gallery)
- Tamati Waka Nene was a Maori warrior and chief from New Zealand in the early 19th century.
- He played a significant role in the interactions between Maori and European settlers in New Zealand, working to establish peaceful relations and to protect Maori land and culture.
- Tamati Waka Nene was depicted in several works of art, including paintings, carvings, and sculptures, many of which were created to commemorate his life and legacy.
- These artworks serve as important visual representations of Tamati Waka Nene and the historical context of his life and the interactions between Maori and European settlers in New Zealand.
- The artistic styles used to depict Tamati Waka Nene reflect the cultural influences present in New Zealand at the time, including elements of Maori, European, and Pacific Island artistic traditions.
- In these artworks, Tamati Waka Nene is often depicted as a strong and proud warrior, with symbols of his rank and status prominently displayed.
- The depiction of Tamati Waka Nene in Pacific Island art provides important insight into the cultural, political, and historical context of New Zealand during the early 19th century, and is an important example of the interactions between cultures in the Pacific Islands.
Navigation chart
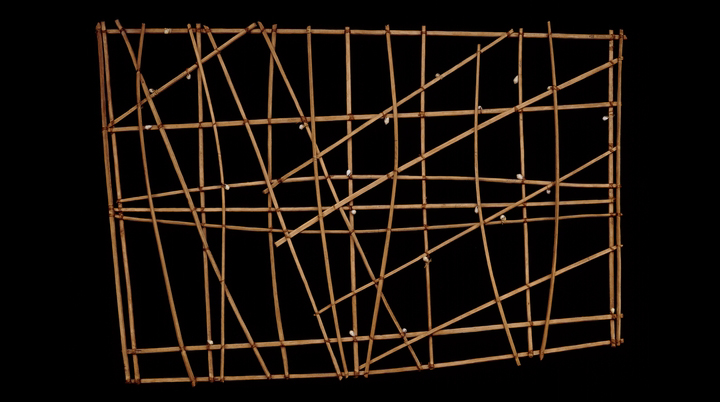
Navigation chart (rebbelib), probably 19th century C.E., wood, shell, 67.5 x 99 x 3 cm, Marshall Islands, Micronesia Trustees of the British Museum
- Navigation charts were used by Pacific Island peoples, including the Polynesians, Micronesians, and Melanesians, to navigate the vast Pacific Ocean and to find their way to new islands and territories.
- These charts were often created on pieces of cloth, bark, or other materials and were often decorated with intricate designs and symbols.
- The navigation charts often incorporated elements of local mythology and cosmology, reflecting the beliefs and cultural practices of the island peoples who created them.
- The use of navigation charts was an important aspect of Pacific Island culture, as they allowed these peoples to explore new territories and to establish trade and cultural exchange with other island communities.
- The navigation charts served as important tools for maintaining and transmitting cultural knowledge from one generation to the next, and are a valuable record of the cultural and navigational practices of Pacific Island peoples.
- The study of Pacific Island navigation charts provides important insight into the cultural, historical, and navigational practices of these island communities, and is an important example of the interactions between cultures in the Pacific Islands.
Presentation of Fijian mats and tapa cloths to Queen Elizabeth II
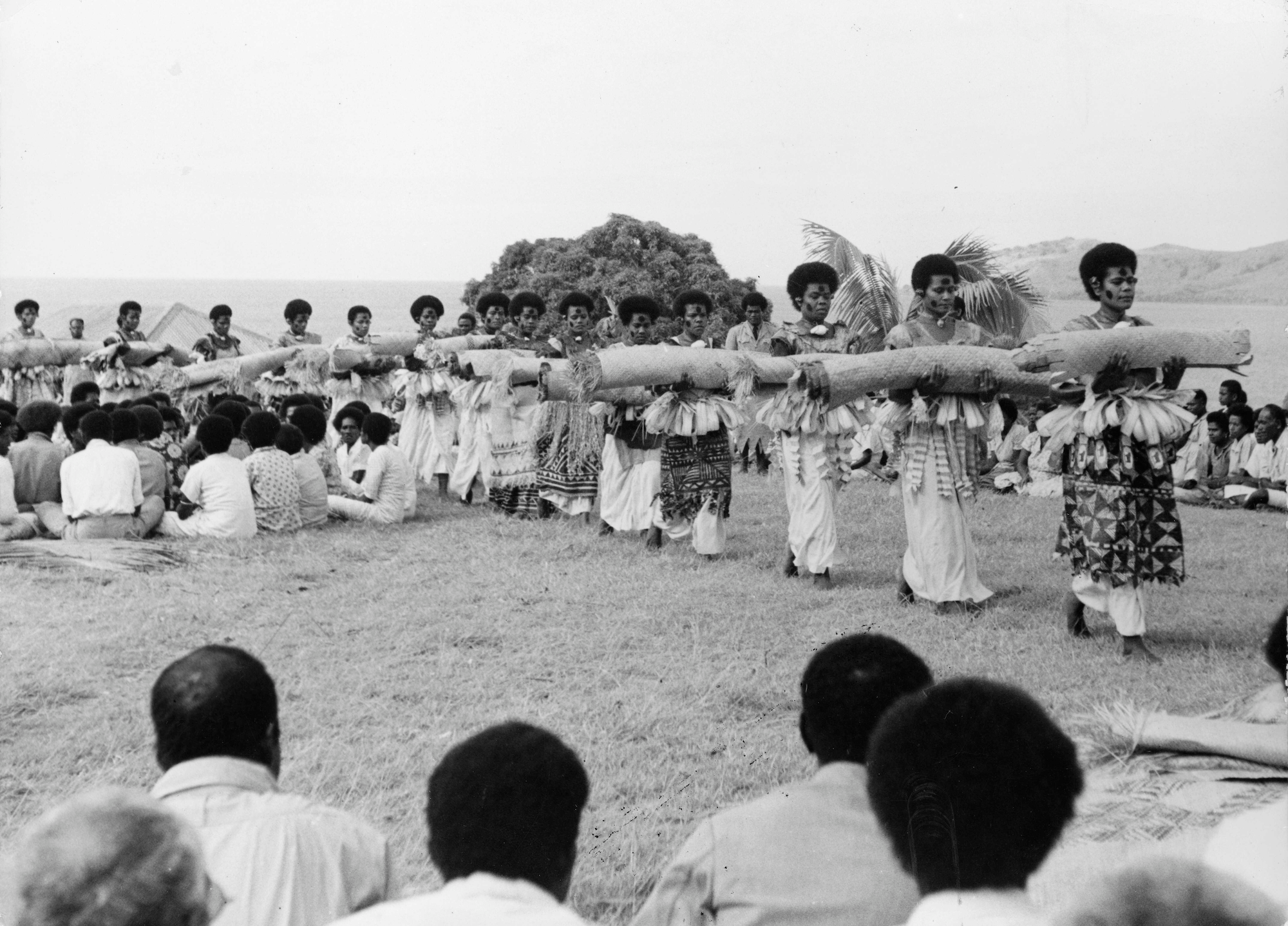

Presentation of Fijian mats and tapa cloths to Queen Elizabeth II during the 1953–54 royal tour, silver gelatin print, 16.5 x 22 cm (Alexander Turnbull Library, Wellington, New Zealand)
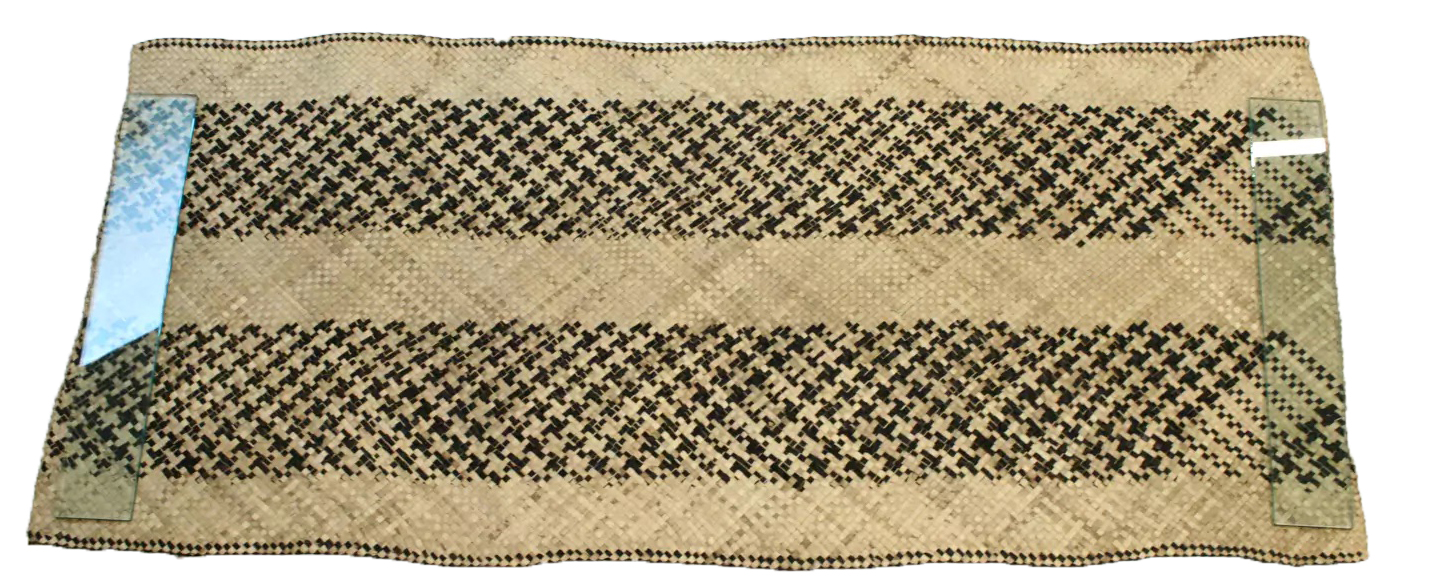

Mat, Fiji, date unknown, pandanus leaf, 176.5 x 77.5 cm (Auckland War Memorial Museum)
- The presentation of Fijian mats and tapa cloths to Queen Elizabeth II was a significant cultural exchange between the Fijian people and the British royal family.

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.